Barhi Date Palm: Cultivation and Characteristics
The Barhi date palm, sometimes called Barhee, is among the popular cultivars of date palms in Iran and worldwide. The history of date palm trees dates back to the emergence of humans, making it challenging to determine the exact origin of each cultivar. However, Iran and Iraq, situated between the Khuzestan province in Iran and Basra city in Iraq, are considered the primary origins of Barhi date palms.

The fruit of the Barhi date is highly favored both in its Khalal (early ripe) and Rutab (ripe) stages. Many countries worldwide consume the fruit during the Khalal stage, known for its intense sweetness and juiciness.
Botanical Classification
The scientific name of this cultivar is Phoenix dactylifera. A mature Barhi date palm typically reaches a height of 5 to 10 meters, although this fluctuation in height results from orchard management practices. Other botanical characteristics, such as stem, leaves, and floral ornamentation, resemble those of other date palm cultivars.
Suitable Soil Conditions for Barhi Date palm
Barhi date palms are generally considered low-maintenance trees and can survive even in poor soils. However, optimal growth and yield occur in soils with better nutrient composition, structure, and texture. The ideal pH for the Barhi date tree ranges from 6.5 to 7.3. Soil with higher alkalinity or limestone content requires pH adjustment using sulfur-containing fertilizers to maintain soil balance.

Proper drainage is crucial for Barhi date palms, as excessive moisture can lead to root rot and susceptibility to various fungal diseases. Under such conditions, rescuing the palm becomes challenging, often resulting in inevitable tree death.
Cultivation Techniques
Barhi date palms thrive in hot, arid climates and can tolerate intense sunlight. They can easily withstand temperatures up to 56 degrees Celsius and require some level of relative humidity, preferably during certain periods of the year. Additionally, they exhibit acceptable yield and growth even in dry air conditions.
Geographical Distribution of Barhi Date Palm Trees in the Middle East
The Barhi date palm tree (Phoenix dactylifera) holds significant cultural and economic importance in the Middle East, particularly in countries like Iran, Iraq, and neighboring regions. Its geographical distribution in the Middle East is influenced by various factors such as climate, soil conditions, and historical cultivation practices.
Iran
Iran stands out as one of the primary regions for Barhi date palm cultivation in the Middle East. The provinces of Khuzestan and Bushehr are notable for their extensive cultivation of Barhi date palms. Cities like Ahvaz, Khorramshahr, and Abadan in Khuzestan province, as well as Ahram, Abpakhsh, and Borazjan in Bushehr province, have significant areas under Barhi date palm cultivation. These regions benefit from suitable climatic conditions, including hot and arid environments with occasional relative humidity, which favors the growth and yield of Barhi date palms.

Iraq
Iraq also holds a prominent position in the geographical distribution of Barhi date palms. The area between the Khuzestan province of Iran and the city of Basra in Iraq is considered one of the primary origins of Barhi date palms. Historical records suggest that this region has been cultivating Barhi date palms for centuries. The cultivation of Barhi date palms continues to thrive in regions like Basra, benefiting from similar climatic conditions as the neighboring Iranian provinces.
Other Middle Eastern Countries
While Iran and Iraq are the main hubs of Barhi date palm cultivation in the Middle East, other countries in MENA also have localized cultivation of this variety. Saudi Arabia, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have favorable conditions for date palm cultivation as Barhi date palm. However, the extent of Barhi date palm cultivation in these countries may vary based on aspects such as water availability, soil conditions, and agricultural practices.
Propagation Methods
The most reliable method for propagating Barhi date palms is tissue culture. This technique ensures the production of Barhi saplings with robust root systems that quickly adapt to orchard soils. It takes a minimum of five years from the tissue-cultured plantation for Barhi date palms to commence fruiting.
Tissue Cultured Barhi
Tissue culture is the best and most reliable method of producing and propagating Date palm trees. You can read the reason for this superiority in the article on date palm production methods. Barhi plants produced by tissue culture have well-built roots and develop quickly in the soil.
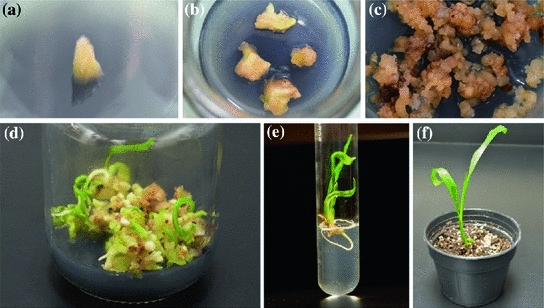
Five years is the minimum time required to fruiting Barhi tissue culture date palm. It means that at least five years must have passed since the planting of tissue culture in the ground for the tree to start bearing fruit.
Barhi Date palm Offshoot
Offshoot planting is one of the propagations of all date palm tree varieties. Identifying and choosing the proper offshoot that has ideal height and weight conditions, the right time and season to identify and the season for separation, as well as the skill of the workforce in separating the sapling from the mother tree are vital points for the propagation of date palm trees using The traditional method of sowing Barhi offshoots.

irrigation systems
The best irrigation methods for date palm trees are drip and subsurface irrigation systems. Since the date palm tree is sensitive to the presence of stagnant water around its trunk and roots, under no circumstances should you use the flooded irrigation method for the date tree. The risk of this method is very high, especially for tissue culture seedlings, and it increases the risk of rotting and fungal diseases.

Rain irrigation is another inappropriate and dangerous irrigation method for date palms. Since in this method, in addition to the surface of the soil, the water also touches the leaves and the central bud (brain or heart of the palm), the accumulation of water and moisture quickly causes the central bud to rot, and the tree dies in a short period.
Pollination
Proper pollination is crucial, especially for the Barhi cultivar, to prevent fruit clustering or “Shaysh,” which often results from incomplete pollination. Manual pollination by skilled individuals using fresh pollen from the same year is recommended. Mechanical pollination with dried pollen is also effective. Weather conditions, such as wind, humidity, and excessive heat should considered to optimize pollination success.
The correct method of pollination depends on several points:
Pollination must be done manually by experienced and skilled people.
Make sure to use fresh pollen from the same year. Mechanical pollination should done with dry pollen.
Barhi Date palm pollination
If there is wind on the day of pollination, pollination should repeated the next day.
Pollination should repeated in case of high humidity or rain.
In case of excessive heat and severe sunlight, pollination must repeated.
For tissue culture varieties, avoid pollination until the fifth year after planting.

Recommended Pollinators (Male trees)
Ghannami male date palms, categorized into Ghannami red and Ghannami green varieties, are the preferred male pollinators for Barhi date palms. However, for other date palm varieties, there is limited verified data on suitable male pollinators. The choice between Ghannami red and green varieties depends on local climatic and geographical conditions. While Ghannami red might perform better in certain regions like Ahvaz and Abadan, overall, there isn’t significant differentiation in performance between these two Ghannami varieties.
